Recently, the teams of Academician Huang Wei, Professor Chen Runfeng and Professor Tao Ye from the State Key Laboratory of Organic Electronics and Information Display of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications have made new progress in the field of organic super afterglow, put forward a simple and effective strategy of subject sensitization and stable isolation of chromophores, developed super afterglow polymers with long life, high efficiency and high color purity, and explored the potential application of such materials in the field of high-resolution afterglow display. On January 30th, the related achievements were published in the international academic journal Nature Communications with the title of “Multicolor Hyperafterflow from Isolated Fluorescence Chromophores”. Professor Tao Ye, Professor Chen Runfeng and Academician Huang Wei from College of Materials Science and Engineering are co-authors, and master student Zhang Xiao is the first author of the paper.
Organic long afterglow usually refers to the phenomenon that organic materials can continue to emit light after the excitation source is removed. This special optical property makes this kind of materials can be used in advanced information encryption and anti-counterfeiting, sensing, afterglow display, biological /X-ray imaging and other fields. In recent years, researchers have made remarkable progress in adjusting the lifetime and luminous color of organic long-lasting materials through crystal engineering, host-guest doping and polymerization. However, due to the large structural relaxation and slow radiation decay process of triplet excitons, the color purity and luminous efficiency of organic long afterglow materials can not meet the requirements of high resolution, high efficiency and wide color gamut display applications. Therefore, it is still an arduous challenge to realize organic super afterglow emission with narrow emission spectrum and high luminous efficiency.
In order to solve this problem, the team led by Academician Huang Wei, Professor Chen Runfeng and Professor Tao Ye put forward the following strategies: combining multiple resonance fluorescent chromophores with narrow-band luminescence characteristics with rigid afterglow host, and successfully preparing a series of colorful super afterglow polymer materials with the narrowest full width at half maximum of 38nm, the highest photoluminescence quantum efficiency of 88.9% and the longest luminescence lifetime of 1.64s through host sensitization and stable isolation of the guest fluorescent chromophores. Thanks to the characteristics of high-efficiency narrow-band afterglow emission and aqueous solution processing of super-afterglow polymer materials, the author explored the applications of such materials in afterglow lighting, high-resolution afterglow display and path display. This research result not only constructs an organic super-afterglow polymer with long life, high efficiency and high color purity, but also provides a simple, effective and universal method to adjust the life, efficiency and color of super-afterglow polymer materials, which is of great guiding significance for the development of high-performance organic super-afterglow luminescent materials, and will also promote the further development of organic long-afterglow materials in the fields of high resolution, high efficiency and wide color gamut afterglow lighting and display applications.
The research results are supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the distinguished professor Plan of Jiangsu Province, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, the “1311 Talent Plan” of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications and the Start-up Fund of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications.
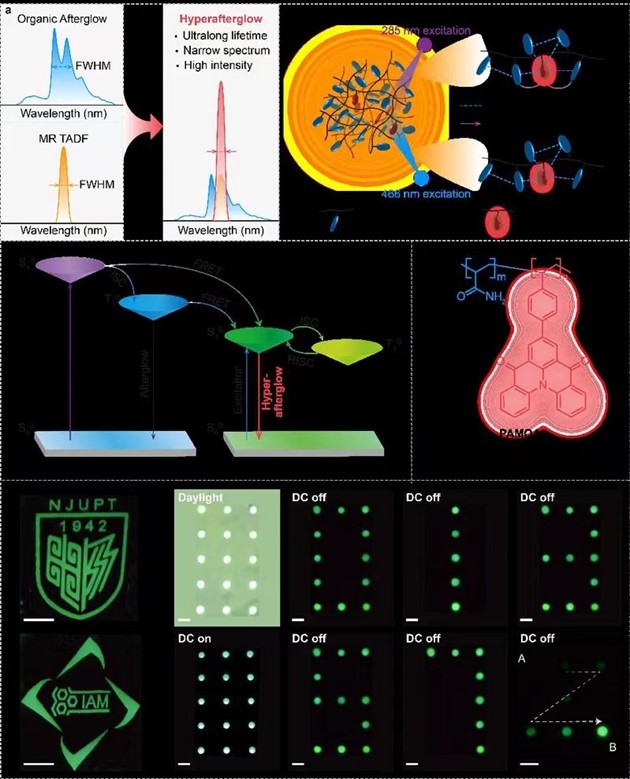
Molecular design strategy and application of organic super afterglow polymer materials
(Writer: Tao Ye Preliminary Reviewer: Zhao Yunyu Editor: Wang Cunhong Final Reviewer: Zhang Feng)



